|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
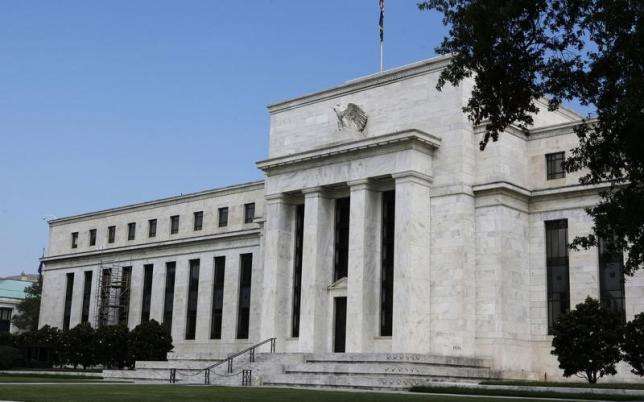
Introduction: On Thursday, the US Federal Reserve took a significant step in its ongoing efforts to stabilize the US economy by reducing its benchmark interest rate by a quarter of a percentage point. This move, widely anticipated by financial experts, marked the latest decision in a series of adjustments aimed at addressing inflation and its impact on the broader economy. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which is responsible for setting the nation’s monetary policy, lowered the overnight interest rate to the range of 4.50%-4.75%. The decision to reduce rates was unanimous, signaling a consistent approach towards managing economic growth and inflation.
H1: The Federal Reserve’s Role in Managing Inflation and Economic Growth
The Federal Reserve plays a central role in the US economy by adjusting interest rates to control inflation and ensure stable growth. With its decision to cut interest rates, the Fed is aiming to strike a balance between promoting economic activity and preventing inflation from rising too quickly. This latest reduction follows a series of rate hikes over the past year, as the Fed sought to cool off inflationary pressures resulting from the post-pandemic recovery and global supply chain disruptions.
H2: Economic Activity Continues to Expand, but Inflation is Still a Concern
According to the Federal Reserve’s policy statement, “Economic activity has continued to expand at a solid pace,” indicating that the US economy is still experiencing growth. However, the statement also reflects the Fed’s ongoing concerns about inflation, which has been a significant issue in recent years. The Fed’s primary objective is to bring inflation down to its target rate of 2%, a goal that remains central to its monetary policy decisions.
Despite the easing of inflationary pressures, price levels remain above the Fed’s desired target, prompting the need for continued adjustments in interest rates. The personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index, excluding food and energy items, has shown limited movement, with a roughly 2.6% annual rate as of September. While this represents progress towards the Fed’s goal, it suggests that inflation is not yet fully under control.
H3: Labor Market Conditions Have Eased, but Unemployment Remains Low
One of the key factors influencing the Fed’s decision to lower interest rates is the state of the US labor market. The job market has shown signs of easing, with job gains slowing down compared to previous months. However, despite this, the unemployment rate remains low, a sign of the overall health of the economy.
The Fed’s statement noted that “labor market conditions have generally eased,” which suggests that while the job market is still strong, it is not experiencing the same rapid growth seen in previous years. This is seen as a positive sign, as the labor market cooling could help reduce wage pressures and contribute to a more sustainable economic environment.
H2: The Impact of US Presidential Election on Federal Reserve Policy
The Federal Reserve’s policy decisions are often influenced by the broader political and economic landscape. With the recent election of Republican President-elect Donald Trump, many analysts are speculating on how his administration might impact the Fed’s future policies. Trump, who campaigned on promises of aggressive trade policies and immigration restrictions, could potentially create a more unpredictable economic environment, affecting inflation, growth, and employment.
While the Fed is expected to maintain its focus on inflation and economic stability, changes in fiscal policies under the new administration could complicate the central bank’s efforts. Trump’s approach to trade tariffs and his stance on immigration could have significant implications for the US economy, potentially influencing the Fed’s ability to navigate the delicate balance of fostering growth while keeping inflation under control.
H3: Federal Reserve’s Approach to Inflation and Economic Growth
The Federal Reserve’s current approach to managing inflation and economic growth is based on a series of careful adjustments to interest rates. By lowering the key interest rate, the Fed is attempting to stimulate borrowing and investment, which in turn can help boost economic activity. At the same time, the Fed is mindful of the potential risks of too much stimulus, which could lead to higher inflation in the long run.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell, who was appointed by Trump during his first term, is expected to hold a press conference to discuss the decision and provide further insight into the economic outlook. Powell’s remarks will be closely watched by investors, as they may offer clues about the Fed’s future direction in light of the changing political landscape.
H2: What This Means for Consumers and Businesses
The interest rate cut by the Federal Reserve is likely to have a range of implications for consumers and businesses across the country. For consumers, lower interest rates can make borrowing cheaper, potentially encouraging spending on big-ticket items like homes and cars. For businesses, the reduced cost of borrowing could encourage investment in new projects, expansion, and hiring.
However, the Fed’s caution about inflation means that these benefits may be tempered by the need for further rate adjustments in the future. While the rate cut is a step in the right direction, it does not signal the end of the Fed’s efforts to control inflation.
FAQs About the Federal Reserve Interest Rate Cut
1. What is the Federal Reserve’s primary goal? The primary goal of the Federal Reserve is to promote stable prices (low inflation) and maximum sustainable employment. These objectives help guide the central bank’s decisions on interest rates and other monetary policies.
2. Why did the Federal Reserve cut interest rates? The Federal Reserve cut interest rates to help support economic growth and bring inflation closer to its 2% target. The decision comes as the job market has eased and inflation has made progress towards the Fed’s goal.
3. How does the Federal Reserve affect my personal finances? The Federal Reserve’s decisions on interest rates can influence borrowing costs, including mortgages, credit cards, and loans. Lower rates generally make borrowing cheaper, while higher rates can make loans more expensive.
4. Will the Federal Reserve continue to cut interest rates? The Federal Reserve may continue to cut interest rates gradually, depending on how inflation and the overall economy evolve. However, they must balance this with the need to keep inflation under control.
5. What impact could President Trump’s policies have on the Federal Reserve? President Trump’s policies, especially in areas like trade and immigration, could create economic uncertainties. The Fed will need to navigate these challenges while maintaining its focus on inflation and employment.
Conclusion
The Federal Reserve’s decision to cut interest rates by 25 basis points is a significant move in its ongoing efforts to balance economic growth with the need to control inflation. As inflation moves closer to the central bank’s 2% target, the Fed will continue to monitor economic conditions and make adjustments as needed. The evolving political landscape under President-elect Donald Trump will add an element of uncertainty, but the Federal Reserve remains committed to its dual mandate of price stability and maximum employment.
MUST READ: